![DrHouse] Diagnostic System Using Sensor Information And Expertise](https://aisholar.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/media/February2025/drhouse.png)
DrHouse] Diagnostic System Using Sensor Information And Expertise
3 main points
✔️ Proposes DrHouse, a diagnostic system that integrates sensor data from smart devices with the latest medical knowledge.
✔️ scrutinizes patient symptoms through a multi-step dialogue and improves the accuracy of diagnosis by sequentially updating the probability of each disease.
✔️ Achieved diagnostic accuracy of up to 18.8% higher than existing methods in an experiment, and received high support from patients and physicians in user evaluations.
DrHouse: An LLM-empowered Diagnostic Reasoning System through Harnessing Outcomes from Sensor Data and Expert Knowledge
written by Bufang Yang, Siyang Jiang, Lilin Xu, Kaiwei Liu, Hai Li, Guoliang Xing, Hongkai Chen, Xiaofan Jiang, Zhenyu Yan
(Submitted on 21 May 2024)
Comments: Published on arxiv.
Subjects: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
code:
The images used in this article are from the paper, the introductory slides, or were created based on them.
Summary
Background
In recent years, virtual doctors utilizing large-scale language models (LLMs) have attracted much attention. However, these systems rely on patients' subjective reports of symptoms, which increases the risk of misdiagnosis. Patient perception of symptoms can be inaccurate or affected by memory biases, which can undermine diagnostic reliability. In addition, many existing LLM-based diagnostic systems have difficulty incorporating the latest medical data and are predominantly simple systems (single-turn QA) with a single question and answer. This can lead to missing potential diseases because additional information needed to make a more accurate diagnosis cannot be collected. Furthermore, these systems do not clearly state the probability or rationale for their diagnostic results, which creates a barrier for physicians and patients to trust the results. Against this background, there is a need to develop more objective and reliable diagnostic systems. Personally, I strongly feel the need for a diagnostic approach that does not rely on subjective patient reports, and I hope that technological advances will help to resolve this issue.
DrHouse Proposal
To overcome these challenges, this paper proposes DrHouse, an LLM-based diagnostic system that combines sensor data with medical knowledge DrHouse has the following three features.
-
Utilize sensor data from smart devices
Data such as heart rate, respiration rate, and sleep patterns acquired from wearable devices and other devices can be incorporated into the diagnostic process to improve the objectivity and accuracy of diagnosis. This allows diagnosis to be based on actual physiological data rather than relying on subjective patient reports. This approach is innovative in that it makes effective use of data collected in daily life and is expected to provide highly accurate diagnoses while reducing the burden on patients. -
Utilize the latest medical databases
We continuously study the latest medical databases such as Up-to-Date and PubMed to improve the quality of diagnosis. This enables diagnosis based on the latest medical knowledge and practice guidelines, making the system flexible and responsive to medical advances. Medical information is updated on a daily basis, and by incorporating the latest findings, the system can be expected to make more appropriate diagnoses and propose treatment plans. -
Introduction of sequential diagnostic algorithms
We have introduced an algorithm that provides an optimal diagnostic process while sequentially evaluating the probability of diagnosis. This allows for the appropriate collection of the necessary information during the diagnostic process to improve the accuracy of the diagnosis. Specifically, the system enhances the accuracy of the diagnosis by obtaining a detailed understanding of symptoms through interaction with the patient and, if necessary, obtaining additional sensor data and laboratory test results. This process is similar to actual clinical practice, where physicians interact with patients as they proceed with diagnosis, and is expected to increase patients' sense of security and confidence.
Results
DrHouse was evaluated on three publicly available medical datasets as well as independently collected datasets and achieved up to 18.8% accuracy over state-of-the-art diagnostic systems. Additionally, in a user study of 20 physicians and 12 patients, 75% of physicians and 91.7% of patients supported the use of DrHouse. These results indicate that DrHouse is useful in real clinical practice and in patients' daily lives. Personally, I am very impressed by the high level of support from both physicians and patients, and feel that this is a major step toward the practical application of DrHouse.
Related Research
LLM-based Virtual Doctors
There are two types of medical diagnostic systems that utilize conventional LLM
- Supervised Fine-tuning of LLM by Supervised Learning
- Examples: Med-PaLM 2, DISC-MedLLM, HuatuoGPT
- These methods allow LLMs to learn medical QA data and diagnostic dialogue data to improve the accuracy of diagnosis.
- Retrieval-based LLM (Retrieval-based LLM)
- Example: LLM-AMT, MedDM
- A method in which a medical database is constructed in advance and the appropriate information is retrieved and answered in response to patient questions.
However, these methods had the following challenges
- Existing methods rely on subjective reports of symptoms and carry a high risk of misdiagnosis.
- Difficulty in incorporating the latest medical data and delays in updating information.
- Many systems are completed with a single question and answer, which prevents a detailed understanding of symptoms.
Proposed Method
DrHouse consists of three main modules that integrate sensor data and medical knowledge.
Knowledge Base Construction
- Collect sensor data from smart devices (e.g., heart rate, respiration rate, sleep score).
- Integrate medical expertise (diagnostic guidelines, medical textbooks) and accumulate up-to-date knowledge.
2. Multi-turn consultation
- Through dialogue with the patient, the symptoms are understood in detail.
- Additional sensor data and test results are acquired as needed to improve diagnostic accuracy.
Diagnostic Algorithm
- The probability of candidate diseases is calculated sequentially to determine the optimal diagnostic process.
- Provides clear explanations to physicians and patients by clearly stating the probability and rationale for each disease.
Experimental Results
Evaluation Data Set
DrHouse was evaluated on the following three public and proprietary medical data sets
- DIALMED (medical interactive data for respiratory, dermatology, and gastroenterology)
- MedDG (17,864 multi-round medical dialogue data)
- KaMed (data on more than 63,000 medical interactions)
In addition, we created a virtual patient profile using our own collected sensor data.
Quantitative Evaluation
DrHouse's diagnostic accuracy outperformed existing LLM-based diagnostic systems by up to 18.8% (see Figure 13 ).
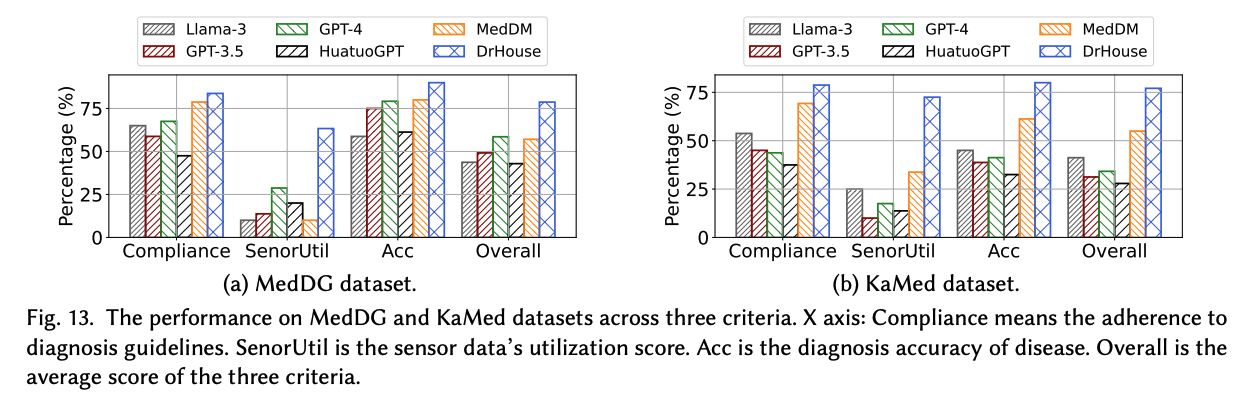
- Accuracy of diagnosis: 18.8% improvement
- Sensor Data Utilization: 34.6% improvement
- Compliance with diagnostic criteria: 9.5% improvement
User Study
- 75% of physicians support the use of DrHouse.
- 91.7% of patients indicated that they would like to use DrHouse.
As these results show, DrHouse is a system that is expected to be used in actual clinical settings.
Conclusion
In this study, we proposed DrHouse, which integrates sensor data and medical expertise to achieve higher accuracy than conventional LLM-based diagnostic systems.
The three main contributions are as follows
- The incorporation of sensor data into the diagnostic process to enable objective diagnosis.
- The use of continuously updated medical knowledge to achieve a diagnosis based on the latest diagnostic criteria.
- The ability to provide a transparent diagnosis, clearly stating the probability and rationale for the diagnosis.
In the future, it is expected that more diverse sensor data will be integrated to develop a system that enables even more advanced diagnosis.
Categories related to this article



![SA-FedLoRA] Communic](https://aisholar.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/media/October2024/sa-fedlora-520x300.png)

![[SpliceBERT] A BERT](https://aisholar.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/media/July2024/splicebert-520x300.png)
![[IGModel] Methodolog](https://aisholar.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/media/July2024/igmodel-520x300.png)