Simulation X Reinforcement Learning! From Simulation To Real Automated Driving Systems (Part 2)
Three main points
✔️ simulation x reinforcement learning
✔️ real-world self-driving tests
✔️ Sim-to-real measures transition successfully
Simulation-Based Reinforcement Learning for Real-World Autonomous Driving
written by Błażej Osiński, Adam Jakubowski, Piotr Miłoś, Paweł Zięcina, Christopher Galias, Silviu Homoceanu, Henryk Michalewski
(Submitted on 29 Nov 2019 (v1), last revised 4 Mar 2020 (this version, v3))
Comments: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)
Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Robotics (cs.RO)
Introduction.
This paper introduces a paper on acquiring a real-life automated driving system by reinforcement learning in simulation. Inputs are RGB images from a camera and semantic segmentation to train a model that outputs steering (steering wheel operation). In our experiments, we have succeeded in transferring the Sim-to-Real driving system.
motivation
In the background of our research, we are motivated by the desire to make effective use of simulations for the construction of real-world automated driving systems.
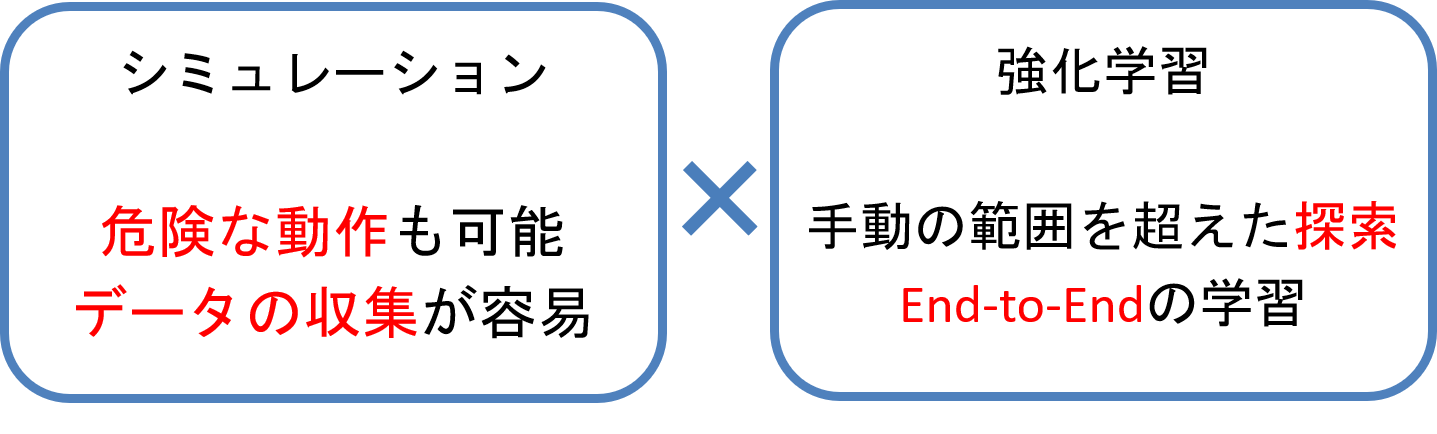
contribution
The contributions of this paper are two
- Testing the effects of visual randomness in simulations
- Testing Self-Driving in the Real World
Visual randomness here refers to changes in the weather or the addition of noise to the image input.
In the first half of my previous article, I described the proposed method, which is an end-to-end model that takes images, semantic segmentation, vehicle metrics (speed, acceleration, and angle), and navigation commands as inputs and steering as outputs, and learns with PPO. We also add noise and other randomization to
This article is about one simulation experiment and seven real-world experiments. Let's have a look at them.
To read more,
Please register with AI-SCHOLAR.
ORCategories related to this article